Conclusion
When I started this series I mentioned that none of the traits explored were either right or wrong. It is clear that they all have their benefits and can have serious negative consequences if not understood and managed. It is obvious that this list is incomplete. It is also true that no one has just one of these traits and indeed we do display each of them under different circumstances.
By understanding that these traits exist and can have beneficial or deleterious effects on the outcome of the project, it helps to understand when the trait should be purposefully employed and when it would be wise to quell the need to engage it.
There are key roles and key moments in the life of a project where the traits described above can benefit the outcome.
Initiation
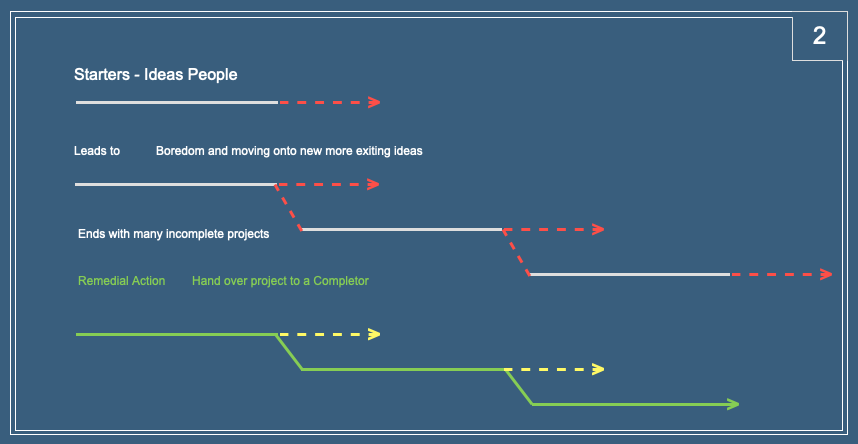
Starters are an obvious positive influence in the creation of a new project. They can see the need for a “thing” to be created and they have enough energy to overcome inertia and bring a project to life.
Obfuscators can help expand ideas producing both wise and slightly mad ideas from which a core theme can be identified and honed in on.
Starter Finishers can help refine the idea and from their knowledge of project delivery can see what ideas are just overly complex or are not essential in the early stages of design. Get them to unify the project to ensure that the goals and objectives are relevant, aligned and meet the original objectives.
Development
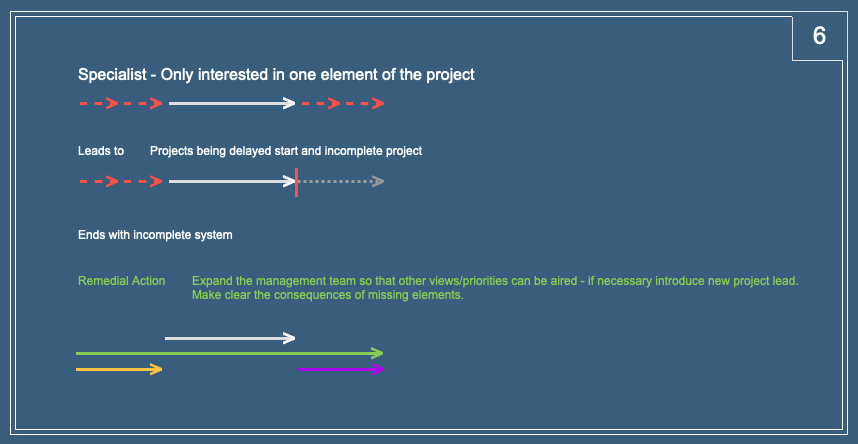
Specialists need to be consulted on what is essential for each aspect of the project. They will quickly identify what is really needed, what has been missed and what is just “fluff”
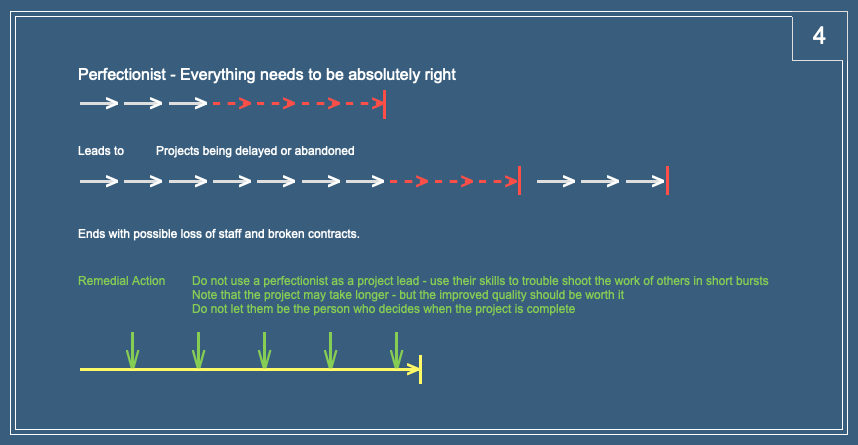
Perfectionists can identify where current systems or designs fail and could be improved.
Get the Starter Finishers to keep things moving and not let things get overly complex or bogged down in detail.
Refinement
As the project evolves, get the Obfuscators back in to check the scope of the project – they will have ideas that are outside of the box. Some of these ideas will be brilliant.
Then get the Specialists back in to refocus on what is still the core of what is needed.
Deployment and Follow-up
This is the time of the Completers. They are good at picking up on lagging energy and willpower. They will produce the checklists that wrap up loose ends and sort out the snagging list until the project is done.
Some projects have a clearly defined conclusion, an end point. Some fade out. Fading out is the nature of software development. It rarely ends with a big party – it ends when the snagging list has been completed. Snagging lists can also become the start of the next project as the previous one hints at what else could be done. This is the start of a new project phase and so back to the initiation phase.
The four missing traits
Saboteur – the reason for the need to sabotage can be illuminating. There is an issue that is not in the open and this may hint at personal issues, personnel issues, at conflicts on strategic decisions and maybe even about morality. They are are worth bringing out into the open as, if they are not seen or handled, the sabotage may succeed.
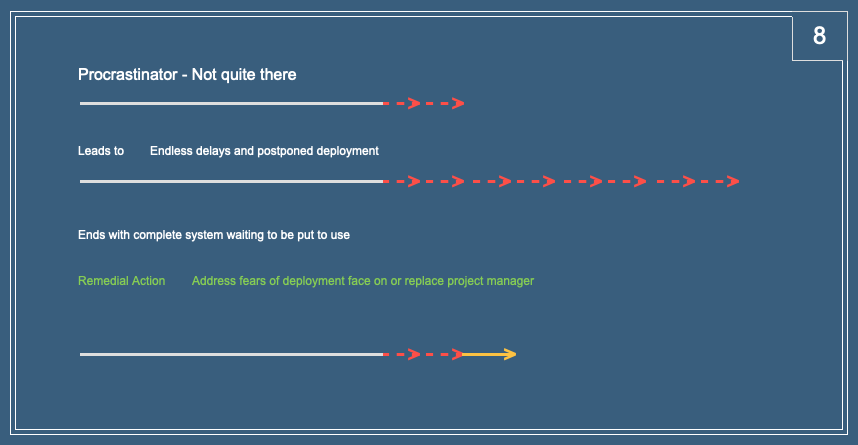
Procrastinator – here the fear may be legitimate. Maybe the reason for holding back reveals a significant risk or, at the very least, a need for further training or counselling. Not handling this situation means the project will result in a loss to all parties.
Confrontation – This can range from passive aggression to outright open warfare. It will not go away. The circumstances that create the conflict need to be explored and handled. If the situation is handled just by removing one side of the conflict, it may well reappear when new team members are recruited.
Swap outs – this is about the best use of scarce and valuable resources or the mishandling of poor resources. When this is about good people who are needed in several places at once, the goal has to be to find more people that have similar traits to the valued staff member and as a matter of urgency. Be clear what those traits are and deliberately seek them in new recruits.
Where a staff member is under-performing then the situation will not be resolved by moving them from one location to another. The manager becomes the saboteur by not handling the personnel issue.